Concepts in Health Science
Introduction to Concepts in Health Science
Health science is a fascinating field that intertwines various disciplines, all aimed at improving human well-being. From understanding the intricate dance of our genes to exploring how societal factors influence health outcomes, this domain offers a wealth of knowledge. As we delve into concepts in health science, we uncover the myriad ways genetics and public health shape our lives.
In today’s world, where information flows freely and healthcare challenges are ever-evolving, grasping these fundamental concepts becomes essential. Whether you’re a student aspiring to enter the field or simply curious about what makes us healthy or unhealthy, there’s something here for everyone. So let’s embark on this enlightening journey through the vital principles informing our health and wellness understanding.
The Role of Genetics in Health
Our health is significantly shaped by our genetic makeup. It influences everything from disease susceptibility to our body’s response to treatment. Each person carries a unique genetic blueprint, which can dictate how they manage illness and wellness.
Inherited traits can determine the likelihood of developing conditions like diabetes, heart disease, or certain cancers. Understanding these genetic factors allows healthcare providers to tailor preventive measures and treatments more effectively.
The emerging field of personalized medicine is revolutionizing how we approach health care. By analyzing an individual’s genetic makeup, clinicians can offer targeted therapies that enhance efficacy while minimizing side effects.
Additionally, genetics interacts with environmental factors. Lifestyle choices such as diet and exercise further complicate this relationship. Recognizing these interactions helps us understand why some people thrive despite similar backgrounds while others struggle with chronic illnesses.
Understanding Public Health and Its Impact on Society

Public health is a vital aspect of societal well-being. It focuses on protecting and improving the Concepts in Health Science of communities through education, policy-making, and research.
One key function of public health is disease prevention. By identifying risk factors in populations, public health professionals can implement programs to mitigate these risks effectively.
Another important area is promoting healthy lifestyles. Initiatives like vaccination campaigns and smoking cessation programs have made significant impacts over the years.
Moreover, public health addresses social inequalities that affect access to care. Understanding how socioeconomic status influences health outcomes allows for targeted interventions.
The collaboration between governmental agencies, healthcare providers, and community organizations enhances overall effectiveness. This collective effort leads to healthier societies and improved quality of life.
In essence, public Concepts in Health Science as the backbone for fostering an environment where individuals can thrive physically and mentally across various demographics.
Key Concepts in Public Health: Epidemiology, Biostatistics, and Environmental Health
Epidemiology serves as the backbone of public health. It investigates how diseases spread, the populations most affected, and what factors contribute to their prevalence. This scientific discipline is crucial for understanding outbreaks and guiding interventions.
Biostatistics complements epidemiology by providing tools for data analysis. It helps researchers interpret complex datasets, making sense of trends in health outcomes over time. Without biostatistics, we would struggle to identify patterns or measure the effectiveness of treatments.
Environmental health focuses on external factors affecting human well-being. From air quality to water safety, this field examines how our surroundings influence health risks. Understanding these environmental impacts is key to developing effective public policies.
Together, these concepts create a comprehensive framework that informs strategies for improving community health and preventing disease outbreaks across diverse populations.
The Importance of Social Determinants of Health
The circumstances in which people are born, grow, live, work, and age are known as social determinants of Concepts in Health Science. These factors significantly influence health outcomes.
Access to quality education plays a crucial role. Individuals with higher educational attainment often enjoy better job opportunities and healthier lifestyles.
Income level is another key factor. Economic stability allows for access to nutritious food, safe housing, and healthcare services.
Community resources also matter deeply. Areas with parks and recreational facilities promote physical activity while neighborhoods with adequate healthcare can lead to earlier diagnosis and treatment of diseases.
Cultural influences shape behaviors too. Understanding cultural backgrounds helps tailor public health initiatives that resonate more effectively within diverse populations.
These elements interact intricately, impacting both individual choices and community wellness as a whole.
Implementing Effective Healthcare Strategies: Prevention and Intervention
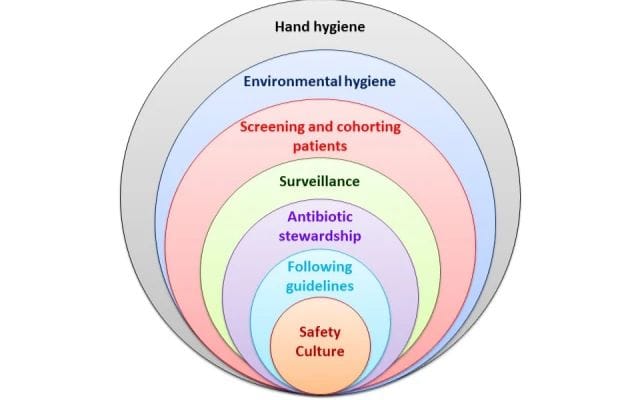
Implementing effective healthcare strategies hinges on a proactive approach to prevention and intervention. By focusing on preventing diseases before they arise, communities can significantly reduce health disparities.
Education plays a crucial role in this process. Public awareness campaigns about healthy lifestyle choices empower individuals to take charge of their well-being. Simple changes, such as improved nutrition and regular exercise, can lead to substantial long-term benefits.
Additionally, targeted interventions are essential for at-risk populations. Programs tailored to specific needs such as mental health services or addiction support serve as critical lifelines.
Collaboration among healthcare providers is vital in creating comprehensive strategies that address various health concerns holistically. By sharing resources and knowledge, these partnerships enhance the effectiveness of both preventive measures and interventions.
Integrating technology into healthcare delivery promises exciting advancements. Telehealth options make it easier for people to access care remotely while still receiving personalized attention from professionals.
Conclusion
The interplay of genetics and public health shapes our understanding of healthcare. Every individual’s biological makeup contributes to their health outcomes, while societal factors play a significant role in shaping those outcomes on a broader scale.
Recognizing the importance of social determinants can transform how we approach health interventions. Acknowledging these influences helps create tailored strategies that resonate with diverse communities.
Innovative healthcare models focus on prevention rather than solely treatment. Emphasizing proactive measures ensures long-term wellness for populations.
As we explore further into concepts in health science, new avenues emerge for research and practice. This dynamic field invites continuous learning and adaptation.
Engagement with multidisciplinary approaches will be crucial as we move forward in improving global health standards. The commitment to integrating various aspects will yield richer insights and more effective solutions for all individuals.
What are the 8 concepts of health?
Concepts in Health Science is a multifaceted concept, with eight key components that form its foundation. These include physical, mental, emotional, social, spiritual, environmental, occupational, and financial health.
Physical health focuses on the body’s well-being. It’s about maintaining fitness and preventing disease through exercise and nutrition.
Mental health encompasses cognitive processes such as thinking and understanding. It has a significant impact on how we manage stress.
Emotional health refers to our ability to manage emotions effectively. This affects relationships with others and ourselves.
Social health emphasizes the importance of supportive networks for overall wellness. Strong connections contribute significantly to happiness.
Spiritual health involves finding purpose and meaning in life beyond material existence.
Environmental health addresses surrounding factors affecting human well-being air quality or access to clean water are prime examples.
Occupational health connects career satisfaction with personal fulfillment while financial stability supports all aspects of living comfortably.
What are the 4 main areas within healthcare science?
Healthcare science encompasses various disciplines, each integral to the delivery of effective health services. The first area is clinical practice, focusing on patient care and treatment. Professionals in this field apply scientific knowledge directly to improve individual health outcomes.
Next is medical technology, which involves the development and application of tools and devices that enhance diagnostics and therapies. This sector drives innovation, leading to better healthcare solutions.
Health informatics represents another vital component. It combines information technology with healthcare to manage patient data efficiently. This ensures accurate record-keeping and improves decision-making processes for providers.
Public health plays a crucial role in advocating for community wellness through disease prevention strategies. Addressing population-level concerns such as access to care or vaccination programs, fosters healthier societies overall. Each area works synergistically within healthcare science to promote optimal health at both individual and societal levels.
What is the list of health concepts?
The world of health science is vast and multifaceted. At its core, it encompasses various concepts that shape our understanding of well-being and medical practice. Here’s a list of essential health concepts:
1. **Health Promotion**: Encouraging healthy behaviors to improve overall wellness.
2. **Disease Prevention**: Strategies aimed at reducing the incidence of disease through vaccinations, screenings, and lifestyle changes.
3. **Epidemiology**: The study of how diseases affect populations, helping to identify risk factors and control outbreaks.
4. **Biostatistics**: Applying statistical methods to analyze data related to public health, guiding decision-making processes.
5. **Public Health Policy**: Developing regulations and laws that protect community health based on scientific evidence.
6. **Environmental Health**: Examining how environmental factors like air quality or water safety impact human health.
7. **Social Determinants of Health**: Understanding how social conditions like socioeconomic status or education affect individual and community health outcomes.
8. **Healthcare Systems Science**: Analyzing healthcare delivery systems for efficiency and effectiveness in meeting population needs.
These concepts are interlinked yet distinct, combining genetics with public policy for a comprehensive approach to healthcare challenges today and into the future.
Understanding these fundamental ideas can empower individuals as well as communities to advocate for better practices in their own lives while influencing broader societal change in pursuit of enhanced public health outcomes.
Exploring these areas helps clarify our roles within the larger framework of health science as we strive for healthier communities worldwide.






